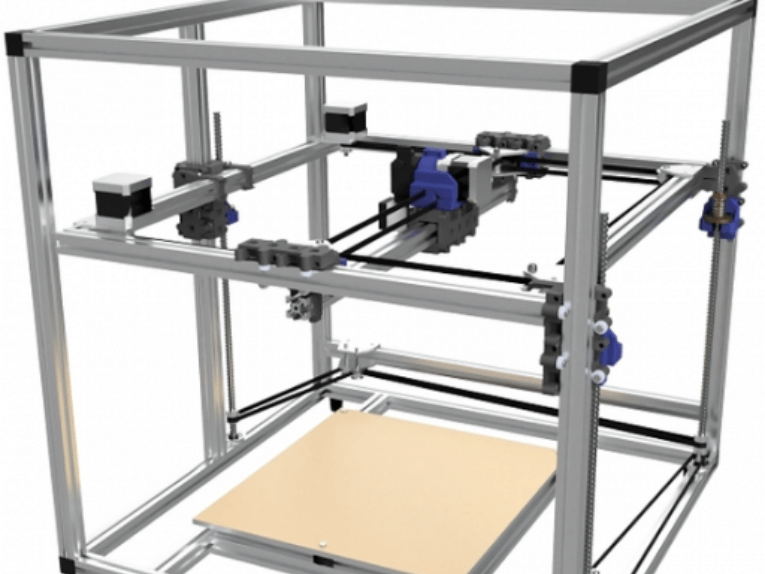
A system of overhead beams in 3D printing is a mechanical structure that prescribes the motion of either the printer’s tool head or a robotic arm along the print area. Most often it will have rails, straps, and motors that work together to control the position of the tool head on X, Y and sometimes Z axes. The rails provide a stable path for movement; belts carry force from motors to the tool head, while precision drives all this assembly by motors. This unified device allows depositing or solidifying material layer by layer with extreme accuracy which makes it possible to manufacture intricate and accurate 3D objects. The gantry system takes charge of smooth and precise movements thereby influencing the quality and dependability of three dimensional printed parts.
Basics of Gantry Systems
It is important to note that gantry systems in 3D printing play a crucial role in ensuring accuracy and repeatability during the manufacturing process. Such systems are basically made up of a set of linear rails and several motors that determine the movement of the print head along the X, Y and sometimes Z axes. This is what allows them to offer great precision on the parts produced, thus making it easy for them to design complex designs and produce small details with ease. The performance of gantry systems can also be enhanced through integration of advanced control software as well as feedback mechanisms, which allow printers to compensate for slight deviations thereby maintaining consistent quality over long print jobs. Furthermore, the choice between aluminum or steel materials for constructing these rails and support structures boosts their overall rigidity and stability hence preventing vibrations or other mechanical stresses from distorting the final prints. Gantry systems optimize motion while preserving structural integrity; they are thus central to modern 3D printers’ functionality and efficiency.
Role of Gantry Systems in 3D Printers
The significance of the gantry system on 3D printers lies in the fact that it determines the accuracy, speed and dependability of the printing process. These systems operate by moving print heads along multiple axes, thus ensuring precision in layer deposition. It is possible to move a print head very precisely and repeatedly using high quality linear rails with powerful stepper or servo motors that contribute to overall print accuracy. Advanced control software supplements these systems and helps them to adapt to minor changes during printing so as to maintain uniformity in outputs. The materials used for constructing the gantry system like aluminum or steel are very strong and help minimize vibrations which can affect the quality of prints. Therefore, this makes gantry system an important aspect of modern 3D printers efficiency and effectiveness.
Gantry vs. Cartesian Systems
In 3D printers, both gantry and Cartesian systems are used to control the print head’s movement. However, they are different in their design and how they operate. In this case, the Cartesian system is based on three linear axes (X, Y and Z) each equipped with own motor and rail. This arrangement is typically less complex and more cost-effective hence widely utilized for many 3D printers.
On the contrary, gantry systems offer improved stability and higher precision resulting from its stiff configuration. Gantry system has a suspended print head that moves along beams parallel to the print bed. Such design reduces the deflection and vibrations affecting print quality thus it suits high-precision applications. Moreover, in most cases gantry systems have large printing volumes as well as capability to bear heavier loads enhancing their versatility.
To sum up, while Cartesian systems tend to be less complicated than other kinds of set ups in most 3D prints, gantry models yield better results for accuracy as well as stability making them relevant for more demanding or industrialized printing jobs.
Post time: Feb-18-2025