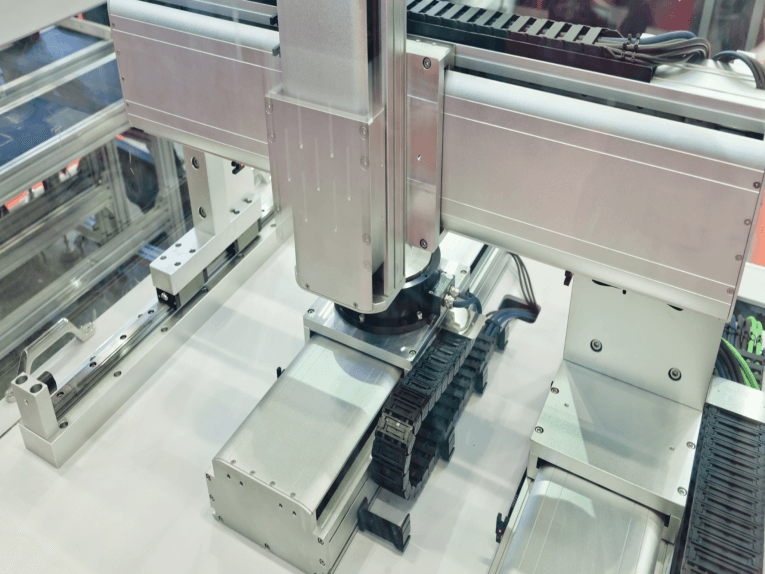
Introduction to Industrial Robots
An industrial robot can be defined as a robot system that is used for manufacturing. A wide range of tasks can be performed by the industrial manufacturing robots as they are included with diverse capabilities.
Industrial robots perform various tasks (such as picking up and clamping activities, spot and arc welding, clamping for machining, manipulation and transfer of parts) with the help of sensors, computer software, and a network of complex mechanical gestures.
Furthermore, industrial robots are automated, programmable and capable of movement in two or more axes. Applications of robots include welding, painting, assembly, pick and place for printed circuit boards, packaging and labeling, palletizing, product inspection, and testing; all accomplished with high endurance, speed, and precision.
A Quick Guide to Definitions
Axis – Axis can be defined as a direction that is used to state the motion of a robot in a linear or rotary mode
Speed – In this case, speed can be defined as the speed of a robot used to position the end of its arm when all axes are moving.
Acceleration – How quickly a robotic arm can pick up the pace
Accuracy – Accuracy can be defined as exactness of a robot on how closely it can reach a commanded position.
Repeatability – How well the robot will return to a programmed position.
Carrying capacity or payload – how much weight a robot can lift
Prismatic Joint: It provides a linear sliding movement between two bodies (it is often called as a slider). It can be formed with a polygonal cross-section to resist rotation.
Kinematics – The actual arrangement of rigid members and joints in the robot, which determines the robot’s possible motions. Classes of robot kinematics include articulated, Cartesian, parallel and SCARA.
Types of Industrial Robots
There are different types of industrial robots based on specifications and applications. Various types of industrial robots include non-servo robots, servo robots, programmable robots, and computer programmable robots.
Non-servo robots: These robots are used to move and place objects. That means, these robots will be capable to pick up an object and transport the object, place it down.
Servo robots: Servo robots include manipulators, effectors, robotic appendages that function as the arms and hands of the robot.
Programmable robots: These robots store commands in a database i.e. they can repeat a task a pre-determined number of times.
Computer programmable robots: These robots are essentially servo robots that can be controlled remotely, via a computer.
Classification by Types of Robots
Robots are mostly classified into five major configurations based on their mechanical structure. They are:
Cartesian robot: Cartesian robot consists of three prismatic joints and axes are concurrent with a Cartesian coordinate system
SCARA robot: SCARA (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm) robot is included with two parallel rotary joints to provide compliance in a plane.
Articulated robot: Articulated robot is a robot whose arm has at least three rotary joints
Parallel robot: A parallel robot is a robot whose arms have concurrent prismatic or rotary joints
Post time: Mar-27-2023