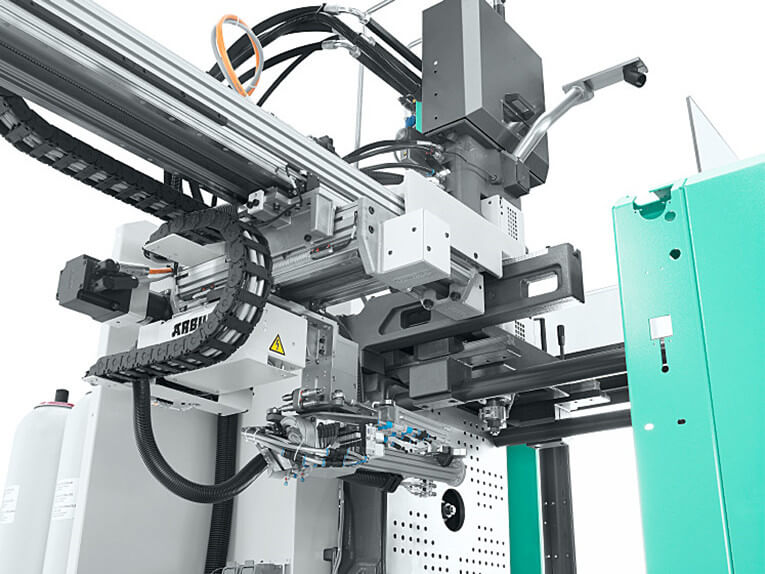
Linear robots are a type of industrial robot that move only in a straight line as opposed to rotating in all directions. They typically feature two or three principal axes and function at right angles to each other.
Linear robots are a highly specialized type of industrial robot that prove highly beneficial in certain applications. Not all environments are conducive to the use of linear robots, but there are advantages to using linear robots in certain scenarios.
The Benefits of Linear Robots
Since linear robots have no rotating axes and are built to only move in one direction, they are typically more accurate than traditional industrial robots. Their mechanical structure inherently limits rotational movements, helping to increase not only the accuracy but also the repeatability of linear robots.
Repeatability is a key attribute of industrial robots and one of their most distinct advantages. Repeatability leads to higher quality products and more consistent products with predictable production volumes.
Linear robots, when used in the correct application, can bring greater product quality and consistency through process repeatability.
Linear Robot Applications
Linear robots’ high levels of repeatability make them most productive in mundane, repetitive tasks. They’re especially well equipped to perform in environments where parts can be presented in a highly consistent, reliable manner where the robot does not need to reposition or recalibrate to locate parts.
Not all applications will benefit from linear robots, but some common industrial applications that do include:
-
Pick and place
-
Sorting
-
Packaging
-
Palletizing
-
Assembly
Linear robots are best for mundane, repetitive tasks where their high levels of repeatability can maximize productivity. While the uses listed above are some of the most common for linear robots, they are far from an exhaustive list of applications that may benefit from linear robots.
Post time: Oct-31-2022