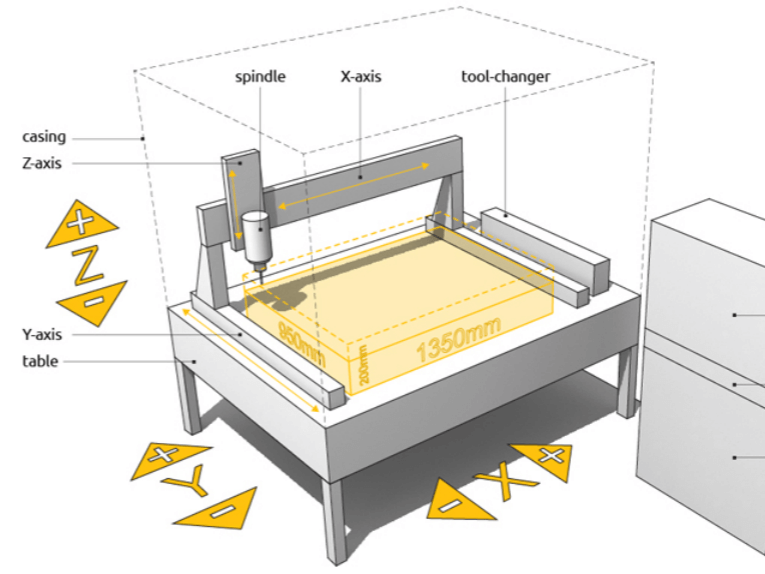
A 3-axis CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine operates by moving a cutting tool or workpiece along three primary axes: X, Y, and Z. The X-axis controls the horizontal movement left to right, the Y-axis manages the horizontal movement front to back, and the Z-axis handles the vertical movement up and down. These machines are programmed through G-code, which dictates precise movements and operations. A controller interprets these instructions, activating motors and drives corresponding to each axis, thereby positioning the tool or workpiece with high precision. This coordinated movement along the three axes enables the machine to perform complex cutting, drilling, and milling tasks, producing detailed and accurate components.
The Basics of 3-Axis CNC Milling
3-axis CNC milling is a machining process that utilizes Computer Numerical Control to manipulate a cutting tool or workpiece along three primary axes: X, Y, and Z. This allows for the creation of detailed and intricate components across various industries.
- 1.Workpiece Movement
- The X-axis handles horizontal movement left to right.
- The Y-axis controls horizontal movement front to back.
- The Z-axis manages vertical movement up and down.
- 2.Toolpath and G-Code Programming
- G-code is the language used to command the CNC machine, detailing every movement and operation.
- Toolpaths must be precisely programmed for each specific task to achieve the desired outcome, whether it’s cutting, drilling, or milling.
- 3.Technical Parameters
- Cutting Speed: Typically measured in surface feet per minute (SFM) or meters per minute (m/min), cutting speed needs to be optimized based on material type and tool diameter.
- Feed Rate: Measured in inches per minute (IPM) or millimeters per minute (mm/min), the feed rate indicates how fast the tool or workpiece moves. Balancing speed and precision is key.
- Spindle Speed: Given in revolutions per minute (RPM), spindle speed must be adjusted according to the material and desired finish quality.
- 4.Material Removal Rate (MRR)
- The MRR is a key performance indicator, calculated by multiplying the feed rate, depth of cut, and width of cut. It determines the efficiency of the milling process.
By understanding and utilizing these parameters, operators can maximize the capabilities of a 3-axis CNC machine, achieving high-precision and quality results efficiently.
Workpiece Movement Along the Three Axes
In addressing the movement of the workpiece along the three axes, it is crucial to comprehend the roles of each axis in a typical 3-axis CNC machine. From my research on the top websites, it’s clear that:
- X-Axis Movement: This axis handles the horizontal movement of the workpiece from left to right. It is essential for accessing different areas of the material in a linear fashion.
- Y-Axis Movement: The Y-axis represents the horizontal movement from front to back. This aids in creating depth and width in the machining process.
- Z-Axis Movement: Managing vertical movement, the Z-axis allows the tool to move up and down. It is vital for making cuts at various depths and performing operations like drilling and milling.
These coordinated movements along the X, Y, and Z axes enable precision machining and versatility in fabricating complex shapes and details in materials.
Post time: Apr-14-2025