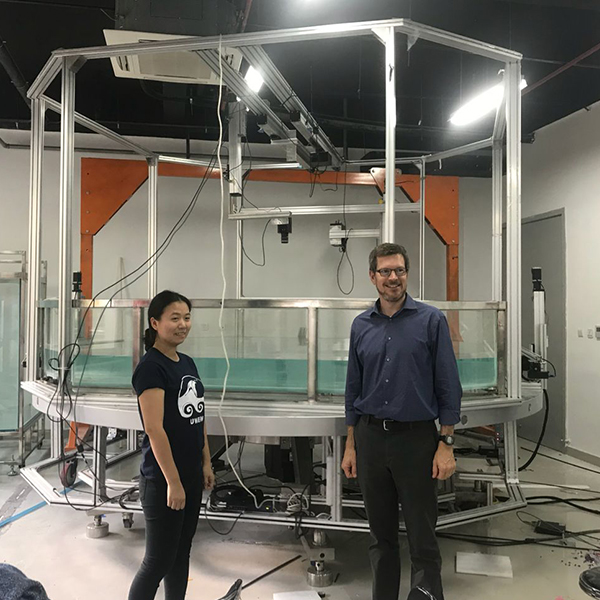
Gantry systems are versatile and can be found in a wide range of applications across various industries. They are particularly popular in manufacturing and assembly processes, material handling, and testing or inspection procedures. The flexibility of gantry systems allows them to be customized to suit specific requirements, which makes them an ideal choice for many different tasks.
Manufacturing and Assembly
Gantry systems play a critical role in manufacturing and assembly processes, where they provide precise positioning and movement of components or tools. In these applications, gantry systems can be used to automate tasks such as welding, machining, pick-and-place, and adhesive dispensing.
In welding applications, for example, gantry systems can be outfitted with welding torches and programmed to perform precise, repeatable welds on large workpieces. The use of gantry systems in welding can significantly improve the speed and quality of the welding process while reducing manual labor and associated risks.
Machining applications, such as milling, drilling, and cutting, can also benefit from the integration of gantry systems. By mounting the machining tool on the gantry, the system can be programmed to perform complex, precise movements, resulting in improved accuracy and reduced cycle times. Additionally, gantry systems can be designed to handle large workpieces or multiple workstations, increasing overall productivity.
In pick-and-place applications, gantry systems can be equipped with vacuum grippers or other end-effectors to accurately position and transport components during the assembly process. This level of automation can significantly reduce manual labor and increase throughput, particularly in industries such as electronics manufacturing, where precision and speed are crucial.
Adhesive dispensing is another application where gantry systems can provide substantial benefits. By mounting a dispensing nozzle onto the gantry, the system can be programmed to apply adhesives, sealants, or other materials with high accuracy and consistency. This level of precision can help ensure the quality and reliability of the final product, while also minimizing waste and reducing production costs.
These examples illustrate the versatility of gantry systems in various manufacturing and assembly applications. By providing precise, automated movement and positioning, gantry systems can improve efficiency, productivity, and the overall quality of products.
Material Handling and Logistics
Gantry systems are widely utilized in material handling and logistics applications, where they are employed to automate the process of moving, lifting, and positioning various types of loads. These applications can be found in industries such as warehousing, distribution centers, and shipping facilities. Gantry systems offer numerous advantages in these environments, including increased efficiency, reduced labor costs, and improved safety.
In warehousing applications, gantry systems can be used to streamline the process of picking, transporting, and storing products. For instance, a gantry system equipped with a vacuum gripper or mechanical gripper can quickly and accurately pick items from shelves, transport them to a designated location, and place them onto a conveyor belt or directly into a storage container. By automating these tasks, gantry systems can significantly reduce the time and effort required for manual picking and handling, leading to improved productivity and reduced labor costs.
Distribution centers and shipping facilities also benefit from the implementation of gantry systems. In these environments, gantry systems can be used to load and unload containers, pallets, or individual items, with high precision and efficiency. By automating these processes, gantry systems can help to minimize product damage, improve worker safety, and increase overall throughput. For example, a gantry system with a payload capacity of 500 kg and a positioning accuracy of ±0.1 mm can consistently and safely handle heavy loads while minimizing the risk of damage due to human error.
Another key advantage of using gantry systems in material handling and logistics applications is their adaptability to different load types and sizes. Gantry systems can be designed with various end-effectors and accessories, such as vacuum grippers, mechanical grippers, or magnetic lifters, to accommodate a wide range of materials and objects. This versatility allows gantry systems to be easily integrated into existing material handling processes, providing an efficient solution for automating various tasks.
In summary, gantry systems play a critical role in material handling and logistics applications, where their speed, accuracy, and versatility enable them to efficiently automate tasks such as picking, transporting, and positioning loads. By implementing gantry systems, industries can significantly improve productivity, reduce labor costs, and enhance overall safety in their material handling and logistics operations.
Robotics and Automation
Gantry systems play a significant role in robotics and automation, where they are often integrated with other robotic components and control systems to perform complex tasks. By leveraging the unique capabilities of gantry systems, such as their high precision, speed, and flexibility, industries can enhance the performance of their robotic systems and achieve a higher level of automation.
In the field of robotics, gantry systems are often combined with articulated robotic arms, allowing for a more extensive range of motion and increased workspace. This combination enables the system to perform tasks that would be difficult or impossible for a standalone robotic arm. For example, a gantry system with a working area of 5 x 10 x 3 meters can be used to extend the reach of a robotic arm with a maximum reach of 3 meters, allowing it to perform tasks across a much larger workspace.
The integration of gantry systems with advanced control systems is another crucial aspect of robotics and automation. By utilizing sophisticated algorithms and sensors, gantry systems can perform tasks with a high level of accuracy and repeatability. For instance, a gantry system equipped with a high-resolution encoder and a feedback control system can achieve a positioning accuracy of up to ±1 µm. This level of precision is essential for applications such as semiconductor manufacturing, where even the slightest misalignment can result in product defects or failures.
Gantry systems also play a vital role in the automation of various industrial processes, such as welding, machining, and inspection. In these applications, gantry systems can be outfitted with specialized end-effectors, such as welding torches, cutting tools, or inspection cameras, to perform a wide range of tasks. For example, a gantry system with a maximum speed of 2 m/s and an integrated vision system can perform high-speed, automated inspections of products on a production line, ensuring quality control and reducing the need for manual inspections.
Another key advantage of using gantry systems in robotics and automation is their scalability and modularity. Gantry systems can be easily expanded or reconfigured to accommodate changing requirements or new applications, providing a cost-effective solution for automation needs. For example, a modular gantry system can be easily reconfigured by adding or removing axis components, allowing for a customizable and adaptable solution that can grow with an organization’s needs.
In conclusion, gantry systems are an integral part of robotics and automation, offering a high level of precision, speed, and flexibility. By integrating gantry systems with other robotic components and advanced control systems, industries can significantly enhance the performance of their robotic systems and achieve greater levels of automation in various applications, such as welding, machining, inspection, and material handling.
Post time: May-13-2024